Blockchain technology has been making waves in various industries, and it’s about time we peeled back the layers to understand its intricacies. So, buckle up and join us on this thrilling journey as I explore the world of Blockchain layers.
What Are Blockchain Layers?
Blockchain layers refer to the different levels of architecture within a blockchain network. These layers interact and work together to ensure the proper functioning of the system, from secure data storage to efficient transactions and smart contracts.
How Many Blockchain Layers Are There?
While there isn’t a set number of layers in every blockchain, most systems have at least four primary layers: Layer 0, Layer 1, Layer 2, and Layer 3. Each layer has specific functions and responsibilities, which we’ll explore in detail below.
Layer by Layer
Now that we’ve got our footing, let’s delve into each layer’s unique characteristics and functions. I will expand on their functionalities and provide examples of projects for each layer, helping even those with no understanding of blockchain to comprehend the article.
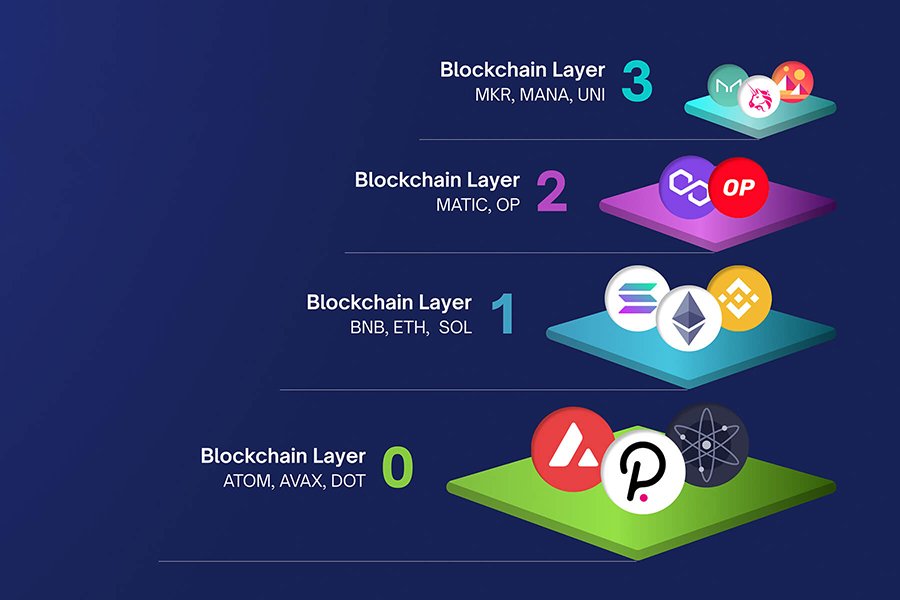
Layer 0: Networking
Layer 0, also known as the networking layer, is the foundation of the blockchain network. It focuses on the communication between nodes and ensures data is transmitted securely and efficiently. This layer uses protocols like TCP/IP and UDP to manage the network infrastructure and maintain its stability.
Examples of Layer 0 projects include Polkadot, Avalanche, Cardano, and Cosmos. These projects aim to improve the interoperability and scalability of blockchain networks, allowing them to communicate with each other and share resources seamlessly. By connecting multiple blockchains, Layer 0 solutions facilitate cross-chain transactions and increase the overall utility of the blockchain ecosystem.
Interoperability Challenges
One of the significant challenges faced by the blockchain industry is the lack of interoperability between different blockchain networks. This limitation has led to the creation of isolated ecosystems, often referred to as “silos,” which hinder the seamless flow of information and value between different platforms.
Layer 0 solutions address this challenge by creating a network of interconnected blockchains, allowing them to share resources and communicate with each other. This enables users to access various blockchain networks without needing to create multiple accounts or use different wallets, providing a more seamless user experience.
Layer 1: Settlement
Layer 1, or the settlement layer, is where the magic happens. This layer is responsible for the core blockchain functions, such as creating and validating blocks, managing consensus algorithms, and maintaining the ledger’s integrity. Layer 1s are blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum that process and finalize transactions on their own blockchain. This layer is crucial for the system’s overall performance and is the backbone of the blockchain network.
In Layer 1, all the technical details, such as block time and dispute resolution, take place. For instance, Bitcoin uses Proof of Work (PoW) as its consensus mechanism, which requires miners to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions. Ethereum, on the other hand, is transitioning from PoW to Proof of Stake (PoS) to improve energy efficiency and scalability.
The Blockchain Trilemma
Layer 1 solutions aim to address the blockchain trilemma, which consists of three core aspects: decentralization, security, and scalability. Decentralization refers to the distribution of control and decision-making power among the network’s participants, reducing the risk of a single point of failure. Security focuses on the robustness of the system and its ability to resist attacks and maintain data integrity. Scalability refers to the network’s capacity to handle increasing transaction volumes without sacrificing performance or efficiency.
However, no single blockchain has nailed all three aspects of the trilemma. Each network faces its unique set of challenges and trade-offs. For instance, Bitcoin is highly decentralized and secure but struggles with scalability, resulting in slow transaction times and high fees. On the other hand, Ethereum has made progress in addressing scalability but is still working on achieving a balance between decentralization and security.
Layer 2: Scaling
Layer 2, or the scaling layer, focuses on enhancing the performance and efficiency of the underlying blockchain network. By offloading some of the processing tasks from Layer 1, Layer 2 solutions help improve the network’s transaction throughput, reduce latency, and lower transaction fees. These solutions often utilize sidechains, state channels, or rollups to achieve their goals.
Examples of Layer 2 projects include the Lightning Network for Bitcoin and the Optimism rollup for Ethereum. These projects aim to provide faster and cheaper transactions by processing them off-chain and only settling the final balances on the main blockchain. This approach significantly reduces the burden on the primary network and enables it to handle a larger volume of transactions.
Layer 2 vs. Layer 1 Scaling
Layer 2 scaling solutions complement Layer 1 efforts in addressing the blockchain trilemma. While Layer 1 focuses on the core blockchain architecture and consensus mechanisms, Layer 2 takes a more application-specific approach to enhance network performance. By working together, Layer 1 and Layer 2 solutions can create a more robust and efficient blockchain ecosystem.
Layer 3: Applications
Layer 3, or the application layer, is where the real-world use cases of blockchain technology come to life. This layer encompasses the various tools, platforms, and services built on top of the underlying blockchain network. From smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps) to digital identity solutions and tokenized assets, Layer 3 is where the possibilities of blockchain technology are truly explored and realized.
Layer 3 Tools and Platforms
Many Layer 3 projects focus on providing tools and platforms for developers to build and deploy their own dApps and smart contracts. Examples include the Ethereum-based Solidity programming language and development frameworks like Truffle, which enable developers to create, test, and deploy smart contracts on various blockchain networks. These tools often simplify the development process, allowing developers to focus on creating innovative solutions without getting bogged down by the underlying technical complexities.
Other Layer 3 projects aim to bridge the gap between traditional finance and the world of blockchain. Decentralized finance (DeFi) is an excellent example of this, as it offers financial products and services built on top of blockchain technology. DeFi platforms enable users to access a wide range of financial instruments, such as lending, borrowing, and trading, without the need for intermediaries like banks or financial institutions.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, blockchain layers play a vital role in shaping the overall functionality and potential of blockchain technology. Each layer has its unique responsibilities and challenges, and by working together, they form a cohesive and efficient system. As the blockchain ecosystem continues to grow and evolve, understanding the importance and functionality of these layers is crucial for anyone looking to leverage the benefits of blockchain technology.
I hope that this guide has provided you with valuable insights into the world of Blockchain layers and their applications. As blockchain technology continues to mature and gain mainstream adoption, the potential for innovation and transformation across various industries is truly limitless.
FAQs
- What are the key benefits of using Blockchain layers?
Blockchain layers provide increased security, transparency, and efficiency in data management and transactions. They enable a decentralized system that is resistant to fraud and censorship. - Can I create my own Blockchain layers?
Yes, you can create your own blockchain layers by building a custom network or using existing platforms like Ethereum and Hyperledger. - What industries can benefit from Blockchain layers?
Industries such as finance, supply chain, healthcare, and real estate can significantly benefit from blockchain technology and its layered architecture. - Are there any drawbacks to using Blockchain layers?
While blockchain technology offers numerous benefits, it also has some limitations, such as high energy consumption, limited scalability, and complex implementation processes. - How can I learn more about Blockchain layers and their applications?
You can learn more about blockchain layers by reading industry blogs, participating in online courses, attending workshops and conferences, and joining relevant communities and forums. - What are some popular Layer 3 projects in the blockchain ecosystem?
Some popular Layer 3 projects include decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms like Uniswap and Aave, decentralized applications (dApps) such as CryptoKitties and Decentraland, and non-fungible token (NFT) marketplaces like OpenSea and Rarible.